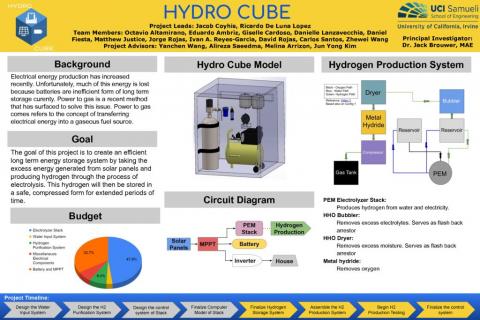
HydroCube
Background
Electrical energy production has increased recently. Unfortunately, much of this energy is lost because batteries are inefficient form of long term storage currently. Power to gas is a recent method that has surfaced to solve this issue. Power to gas comes refers to the concept of transferring electrical energy into a gaseous fuel source.
In an effort to maximize the use of solar energy we seek a power to gas energy storage system such as electrolysis. By using excess solar energy, when a home battery is already full, to power an electrolysis device. Hydrogen produced by such device can be used for home appliances or to produce electricity when the sun is down. This will allow for a fully green home when such technology can be made more efficient.
Goal
The goal of this project is to create an efficient long term energy storage system by taking the excess energy generated from solar panels and producing hydrogen through the process of electrolysis. This hydrogen will then be stored in a safe, compressed form for extended periods of time.
Team Website
https://sites.uci.edu/hydrocube/
Contact
Jacob Coyhis (jcoyhis@uci.edu)
Ricardo De Luna (rdelunal@uci.edu)
Advisor:Jack Brouwer (jb@nfcrc.uci.edu)