Fuel Cell Battery
Background
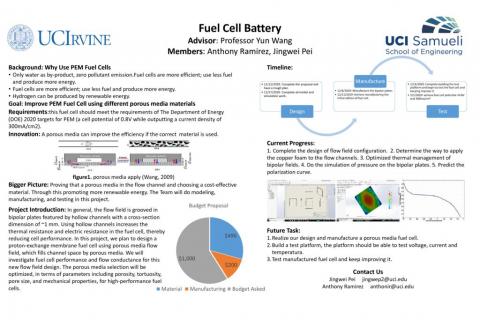
Flow field bipolar plate is a very important part of the proton-exchange membrane fuel cell(PEM). They are designed to provide an adequate amount of the reactants (hydrogen and oxygen) to the gas diffusion layer (GDL) and catalyst surface meanwhile remove the generated water. In general, the flow field is grooved in bipolar plates featured by hollow channels with a cross-section dimension of ~1 mm. Using hollow channels increases the thermal resistance and electric resistance in the fuel cell, thereby reducing cell performance. In this project, we plan to design a proton-exchange membrane fuel cell using porous media flow field, which fills channel space by porous media. We will investigate fuel cell performance and flow conductance for this new flow field design. The porous media selection will be optimized, in terms of parameters including porosity, tortuosity, pore size, and mechanical properties, for high-performance fuel cells.
Goals and objectives
Our goal is to finally complete the design of a proton-exchange membrane fuel cell, we should apply metal foam to the channels region to improve its performance. this fuel cell should meet the requirements of The Department of Energy (DOE) 2020 targets for PEM (a cell potential of 0.8V while outputting a current density of 300mA/cm2). We plan to complete the design in three quarters.
Team Contact
Jingwei Pei
Anthony Lsaiah Ramirez
Advisor
Professror Yun Wang